In today’s fast-paced and competitive business landscape, organizations are constantly seeking ways to enhance efficiency, streamline operations, and make more informed decisions. One of the critical tools that have emerged to address these challenges is Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems. These systems are sophisticated software solutions designed to integrate and manage various business processes, making them a crucial component in the arsenal of modern businesses. In this comprehensive overview, we will delve into the world of these systems, exploring their historical evolution, key components, benefits, challenges, and future prospects.
Historical Evolution of ERP Systems
The journey of enterprise resource management systems traces back to the early 1960s when businesses started automating their processes using computers. However, it was not until the 1990s that these systems as we know them today began to take shape. The first generation of ERP systems primarily focused on automating and standardizing finance-related processes. Over the years, ERP systems evolved to encompass a broader range of functions, including human resources, supply chain management, and customer relationship management.
Key Components of ERP Systems
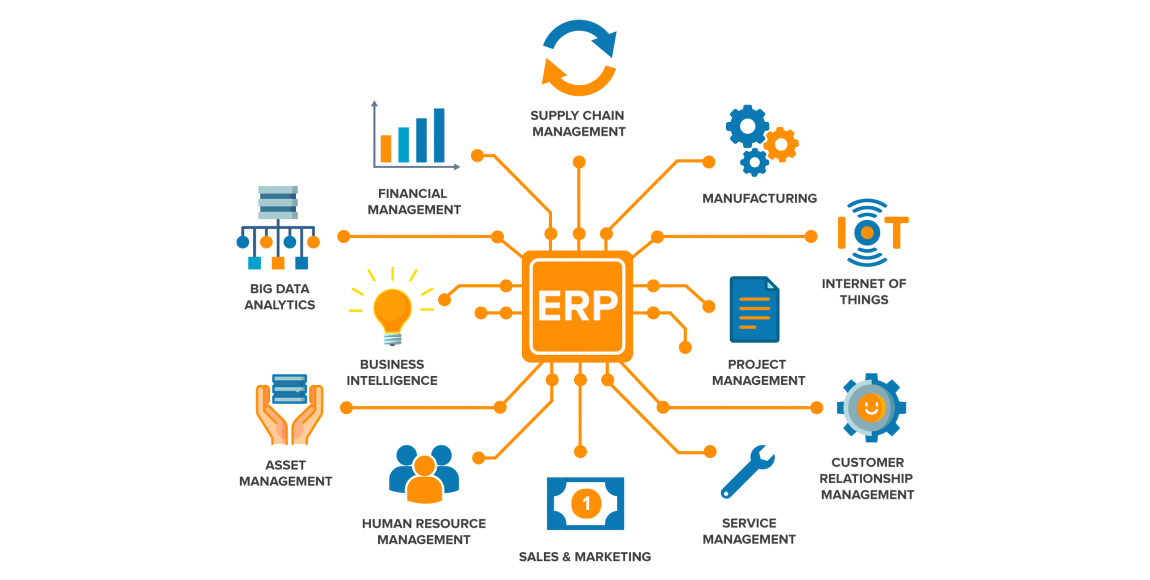
Today’s enterprise resource management systems consist of various interconnected modules that cover a broad spectrum of business operations. These modules can be broadly categorized into core and ancillary modules.
Core Modules:
1. Financial Management: This module automates financial processes, including accounting, budgeting, and financial reporting, ensuring accurate and real-time financial data.
2. Human Resources: HR modules manage employee information, payroll, benefits administration, and performance evaluations, streamlining workforce management.
3. Supply Chain Management: These systems help optimize the supply chain by managing procurement, inventory, production, and distribution processes, leading to improved efficiency and cost savings.
4. Customer Relationship Management: CRM modules enable businesses to track customer interactions, manage leads, and provide personalized customer service, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Ancillary Modules:
1. Business Intelligence: Enterprise resource management systems incorporate advanced analytics and reporting tools to help businesses gain actionable insights from their data, facilitating data-driven decision-making.
2. E-commerce Integration: Many of these systems now include e-commerce modules that allow businesses to seamlessly integrate online sales channels with their back-end operations.
3. Workflow Automation: Automation of repetitive tasks and processes through workflow modules increases operational efficiency and reduces the risk of human error.
Integration and Data Flow:
One of the defining features of enterprise resource management systems is their ability to integrate data and processes across different departments and functions within an organization. This integration ensures a seamless flow of information, eliminating data silos and enabling cross-functional collaboration.
Benefits of ERP Systems
The adoption of ERP systems offers a multitude of benefits to modern businesses:
1. Improved Operational Efficiency: ERP systems streamline business processes, reduce manual tasks, and eliminate redundancy, leading to increased productivity and efficiency.
2. Enhanced Data Accuracy and Accessibility: Centralized data storage and real-time updates ensure data accuracy, while authorized users can access relevant information easily.
3. Streamlined Communication: These systems facilitate communication and collaboration among departments, enabling better coordination and faster decision-making.
4. Better Decision-Making: With access to real-time data and advanced reporting tools, decision-makers can make informed choices, driving the company’s strategic direction.
5. Cost Reduction and ROI: By optimizing processes, reducing errors, and minimizing inventory holding costs, enterprise resource management systems often result in significant cost savings and a positive return on investment (ROI).
Challenges in Implementing ERP Systems
While ERP systems offer a wide array of benefits, their implementation is not without challenges:
1. High Initial Costs: Acquiring and implementing these systems can be expensive, including licensing, hardware, and consulting fees.
2. Data Migration and Integration: Migrating existing data and integrating it into the new system can be complex and time-consuming.
3. Resistance to Change: Employees may resist adopting new processes and systems, leading to resistance and potential disruptions.
4. Ongoing Maintenance and Support: ERP systems require continuous maintenance, updates, and support to remain effective.
5. Security Concerns: As enterprise resource management systems store critical business data, they are prime targets for cyberattacks, requiring robust security measures.
Modern ERP Trends and Innovations
To stay relevant and address evolving business needs, these systems have undergone significant transformations in recent years. Some notable trends and innovations include:
1. Cloud-Based ERP Systems: Cloud-based ERP solutions offer scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, making them increasingly popular among businesses of all sizes.
2. Mobile ERP Accessibility: Mobile applications enable employees to access these systems from anywhere, enhancing productivity and real-time decision-making.
3. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Integration: AI and ML are being used to enhance predictive analytics, automate routine tasks, and improve decision-making within ERP systems.
4. Industry-Specific Customization: Enterprise resource management vendors now offer industry-specific templates and modules, allowing businesses to tailor their systems to their unique needs.
5. Sustainability and Green ERP: Companies are increasingly adopting these systems to support sustainability initiatives by tracking and managing their environmental impact.
Future Prospects of ERP Systems
The future of these systems holds promising possibilities:
1. Evolving Business Needs: Enterprise resource management will continue to adapt to the changing needs of businesses, accommodating emerging industries and technologies.
2. Emerging Technologies Impacting ERP: Technologies like blockchain, 5G, and IoT are expected to further enhance ERP systems’ capabilities.
3. Predictions for the ERP Landscape: Experts predict how ERP systems will evolve over the next decade and their potential impact on businesses.
Best Practices for Selecting and Implementing ERP Systems
To ensure a successful enterprise resource management implementation, businesses should follow best practices:
1. Needs Assessment and Planning: Conduct a thorough analysis of business needs and establish clear goals before selecting an enterprise resource management.
2. Vendor Selection Criteria: Evaluate ERP vendors based on factors such as functionality, scalability, support, and cost.
3. Project Management and Timelines: Implement a structured project management approach with well-defined timelines and milestones.
4. User Training and Change Management: Invest in comprehensive training programs and change management strategies to facilitate user adoption.
Conclusion
Enterprise Resource Planning systems have come a long way since their inception, evolving into indispensable tools for modern businesses. With their ability to streamline operations, enhance data accuracy, and improve decision-making, enterprise resource management systems play a vital role in the success of organizations across industries. While challenges exist in their implementation, the benefits far outweigh the drawbacks. As technology continues to advance, enterprise resource management will adapt and remain central to businesses seeking efficiency and competitiveness in a dynamic marketplace. Embracing enterprise resource management is not just a choice; it’s a necessity for thriving in the modern business landscape.




