Strategic Evolution: A Comprehensive Guide for SAP Upgrade and Migration
- Highbar Technocrat
- Blogs
- December 25, 2023
Connect With Us
Strategic Evolution: A Comprehensive Guide for SAP Upgrade and Migration
- Highbar Technocrat
- Blogs
- December 25, 2023
Connect With Us

It is essential to stay up-to-date with the most recent developments in the constantly changing field of enterprise technology. Upgrading and moving to newer versions is a strategic necessity for companies whose ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) needs are met by SAP (Systems, Applications, and Products) in data processing.
This blog aims to provide a comprehensive guide to SAP upgrade and migration, exploring the reasons, challenges, and best practices for a seamless transition.
Why Upgrade and Migrate?
Upgrading and migrating SAP is a strategic decision undertaken by organizations for several compelling reasons.
Here are some benefits of upgrading to the latest versions of SAP:
Latest Features and Innovations:
One of the primary reasons for upgrading SAP is to gain access to the latest features and innovations. Each new version of SAP brings enhanced functionalities, improved user interfaces, and innovative technologies that can significantly boost efficiency and productivity.
Compliance and Security:
As technology advances, so do security threats and regulatory requirements. Upgrading SAP ensures that your system is equipped with the latest security patches and compliance features, reducing the risk of vulnerabilities and ensuring adherence to industry regulations.
Performance Optimization:
Newer versions of SAP often come with performance optimizations and efficiency improvements. Upgrading allows businesses to take advantage of these enhancements, resulting in faster processing times, improved system responsiveness, and an overall better user experience.
Vendor Support and End-of-Life Concerns:
Regular SAP upgrades ensure continued vendor support. Running on outdated versions may lead to the loss of vendor support, making it challenging to receive critical updates, patches, and assistance in case of issues. Additionally, older versions eventually reach their end-of-life, making an upgrade essential for ongoing system stability.
Compatibility with Other Systems:
With evolving IT landscapes, ensuring compatibility between SAP and other integrated systems is crucial. Upgrading SAP helps in maintaining seamless interoperability with other applications, databases, and technologies within the organizational ecosystem.
Challenges in SAP Upgrade and Migration
While the benefits of upgrading and migrating to newer SAP versions are evident, the process comes with its own set of challenges. Understanding and addressing these challenges is key to a successful transition.
Downtime and Business Disruption:
Upgrading SAP often requires system downtime, which can impact regular business operations. Minimizing downtime and ensuring a smooth transition is a critical challenge that businesses must navigate.
Data Migration Complexity:
Migrating data from an older SAP version to a newer one is a complex task. Ensuring data integrity, accuracy, and completeness during the migration process is a challenge that organizations need to address meticulously.
Customization and Integration:
Many organizations have customized their SAP environments to align with specific business processes. Upgrading SAP may necessitate adjustments to these customizations and integrations, requiring careful planning to avoid disruptions.
User Training and Adaptation:
New SAP versions often come with changes in user interfaces and functionalities. Ensuring that users are adequately trained and can adapt to the changes is crucial for a successful upgrade.
Testing and Quality Assurance:
Thorough testing is essential before implementing any SAP upgrade or migration. Testing helps identify potential issues, ensures compatibility with existing systems, and minimizes the risk of errors during the actual migration.
Budgetary Considerations:
Upgrading SAP is an investment, and organizations need to allocate budgets for both the software licenses and the implementation process. Budgetary constraints can pose a challenge, requiring careful financial planning.
Change Management:
Managing change successfully is crucial when it comes to SAP upgrades. For the transition to go smoothly, it is necessary to make sure that all of the organization’s stakeholders are aware of the changes, involved, and ready.
Best Practices for SAP Upgrade and Migration
To overcome the challenges associated with SAP upgrades and migrations, organizations can follow these best practices:
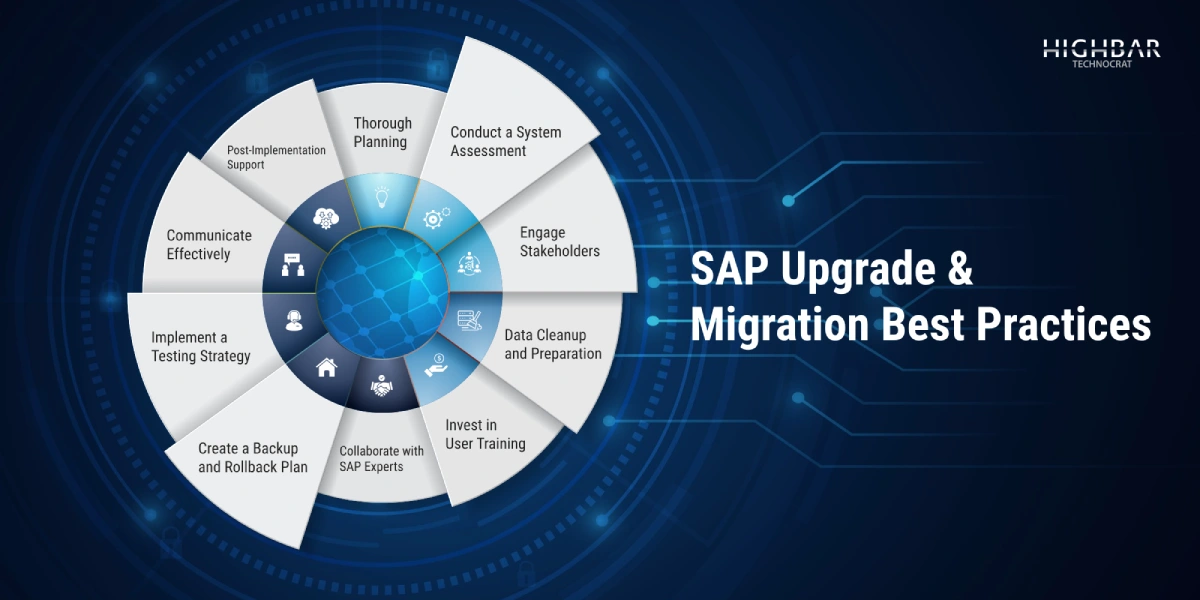
Thorough Planning:
Successful SAP upgrades start with thorough planning. Develop a comprehensive roadmap that outlines the entire upgrade process, including timelines, milestones, and resource requirements.
Conduct a System Assessment:
Before initiating the upgrade, conduct a thorough assessment of the existing SAP system. Identify areas that require improvement, potential bottlenecks, and any customizations that may impact the upgrade.
Engage Stakeholders:
Involve key stakeholders from various departments in the planning and decision-making processes. Their insights can be valuable in identifying specific needs and ensuring that the upgrade aligns with overall business objectives.
Data Cleanup and Preparation:
Prior to migration, ensure that the data in the existing SAP system is clean, accurate, and up-to-date. This reduces the likelihood of issues during the migration process and ensures that the new system starts with reliable data.
Invest in User Training:
To ensure a seamless transition, user training is essential. Invest in in-depth training courses to familiarize users with the latest features, functions, and adjustments in the SAP system upgrade. This minimizes disruptions and ensures a quick adaptation to the new environment.
Create a Backup and Rollback Plan:
Before initiating the upgrade, create a backup of the existing SAP system. Additionally, develop a rollback plan in case any issues arise during the upgrade process. This ensures that the organization can revert to the previous state if necessary.
Collaborate with SAP Experts:
Work together with consultants and SAP specialists who have upgraded systems before. Their knowledge and experience can be used to successfully manage upgrades, reduce risks, and handle challenging situations.
Implement a Testing Strategy:
Develop a robust testing strategy that includes various scenarios, from basic functionalities to complex business processes. Testing should cover data migration, system integrations, and user acceptance to identify and address potential issues before the actual upgrade.
Communicate Effectively:
Transparent and effective communication is key throughout the upgrade process. Keep stakeholders informed about the progress, timelines, and any changes to expectations. This helps manage expectations and fosters a collaborative approach to the upgrade.
Post-Implementation Support:
Provide adequate post-implementation support to address any issues that may arise after the upgrade. This includes monitoring the system’s performance, addressing user queries, and ensuring a smooth transition to the upgraded environment.
Conclusion
Connect With Us
Comments
Highbar Technocrat
It is essential to stay up-to-date with the most recent developments in the constantly changing field of enterprise technology. Upgrading and moving to newer versions is a strategic necessity for companies whose ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) needs are met by SAP (Systems, Applications, and Products) in data processing.
This blog aims to provide a comprehensive guide to SAP upgrade and migration, exploring the reasons, challenges, and best practices for a seamless transition.
Why Upgrade and Migrate?
Upgrading and migrating SAP is a strategic decision undertaken by organizations for several compelling reasons.
Here are some benefits of upgrading to the latest versions of SAP:
- Latest Features and Innovations:
One of the primary reasons for upgrading SAP is to gain access to the latest features and innovations. Each new version of SAP brings enhanced functionalities, improved user interfaces, and innovative technologies that can significantly boost efficiency and productivity.
- Compliance and Security:
As technology advances, so do security threats and regulatory requirements. Upgrading SAP ensures that your system is equipped with the latest security patches and compliance features, reducing the risk of vulnerabilities and ensuring adherence to industry regulations.
- Performance Optimization:
Newer versions of SAP often come with performance optimizations and efficiency improvements. Upgrading allows businesses to take advantage of these enhancements, resulting in faster processing times, improved system responsiveness, and an overall better user experience.
- Vendor Support and End-of-Life Concerns:
Regular SAP upgrades ensure continued vendor support. Running on outdated versions may lead to the loss of vendor support, making it challenging to receive critical updates, patches, and assistance in case of issues. Additionally, older versions eventually reach their end-of-life, making an upgrade essential for ongoing system stability.
- Compatibility with Other Systems:
With evolving IT landscapes, ensuring compatibility between SAP and other integrated systems is crucial. Upgrading SAP helps in maintaining seamless interoperability with other applications, databases, and technologies within the organizational ecosystem.
Challenges in SAP Upgrade and Migration
While the benefits of upgrading and migrating to newer SAP versions are evident, the process comes with its own set of challenges. Understanding and addressing these challenges is key to a successful transition.
- Downtime and Business Disruption:
Upgrading SAP often requires system downtime, which can impact regular business operations. Minimizing downtime and ensuring a smooth transition is a critical challenge that businesses must navigate.
- Data Migration Complexity:
Migrating data from an older SAP version to a newer one is a complex task. Ensuring data integrity, accuracy, and completeness during the migration process is a challenge that organizations need to address meticulously.
- Customization and Integration:
Many organizations have customized their SAP environments to align with specific business processes. Upgrading SAP may necessitate adjustments to these customizations and integrations, requiring careful planning to avoid disruptions.
- User Training and Adaptation:
New SAP versions often come with changes in user interfaces and functionalities. Ensuring that users are adequately trained and can adapt to the changes is crucial for a successful upgrade.
- Testing and Quality Assurance:
Thorough testing is essential before implementing any SAP upgrade or migration. Testing helps identify potential issues, ensures compatibility with existing systems, and minimizes the risk of errors during the actual migration.
- Budgetary Considerations:
Upgrading SAP is an investment, and organizations need to allocate budgets for both the software licenses and the implementation process. Budgetary constraints can pose a challenge, requiring careful financial planning.
- Change Management:
Managing change successfully is crucial when it comes to SAP upgrades. For the transition to go smoothly, it is necessary to make sure that all of the organization’s stakeholders are aware of the changes, involved, and ready.
Best Practices for SAP Upgrade and Migration
To overcome the challenges associated with SAP upgrades and migrations, organizations can follow these best practices:
- Thorough Planning:
Successful SAP upgrades start with thorough planning. Develop a comprehensive roadmap that outlines the entire upgrade process, including timelines, milestones, and resource requirements.
- Conduct a System Assessment:
Before initiating the upgrade, conduct a thorough assessment of the existing SAP system. Identify areas that require improvement, potential bottlenecks, and any customizations that may impact the upgrade.
- Engage Stakeholders:
Involve key stakeholders from various departments in the planning and decision-making processes. Their insights can be valuable in identifying specific needs and ensuring that the upgrade aligns with overall business objectives.
- Data Cleanup and Preparation:
Prior to migration, ensure that the data in the existing SAP system is clean, accurate, and up-to-date. This reduces the likelihood of issues during the migration process and ensures that the new system starts with reliable data.
- Invest in User Training:
To ensure a seamless transition, user training is essential. Invest in in-depth training courses to familiarize users with the latest features, functions, and adjustments in the SAP system upgrade. This minimizes disruptions and ensures a quick adaptation to the new environment.
- Create a Backup and Rollback Plan:
Before initiating the upgrade, create a backup of the existing SAP system. Additionally, develop a rollback plan in case any issues arise during the upgrade process. This ensures that the organization can revert to the previous state if necessary.
- Collaborate with SAP Experts:
Work together with consultants and SAP specialists who have upgraded systems before. Their knowledge and experience can be used to successfully manage upgrades, reduce risks, and handle challenging situations.
- Implement a Testing Strategy:
Develop a robust testing strategy that includes various scenarios, from basic functionalities to complex business processes. Testing should cover data migration, system integrations, and user acceptance to identify and address potential issues before the actual upgrade.
- Communicate Effectively:
Transparent and effective communication is key throughout the upgrade process. Keep stakeholders informed about the progress, timelines, and any changes to expectations. This helps manage expectations and fosters a collaborative approach to the upgrade.
- Post-Implementation Support:
Provide adequate post-implementation support to address any issues that may arise after the upgrade. This includes monitoring the system’s performance, addressing user queries, and ensuring a smooth transition to the upgraded environment.
Conclusion
SAP upgrade and migration are essential components of keeping pace with technological advancements and ensuring that ERP systems align with organizational goals. While challenges exist, the benefits of improved functionalities, enhanced security, and compliance far outweigh the complexities involved. By following best practices, engaging stakeholders, and investing in thorough planning and testing, organizations can navigate the upgrade process successfully and position themselves for continued success in the ever-evolving landscape of enterprise technology.